
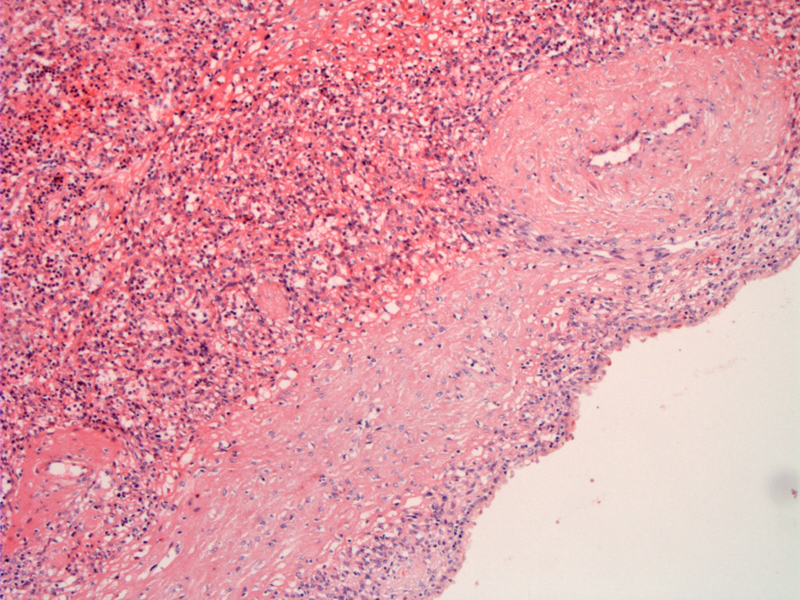
Normal spleen (left) is seen with a fibrotically thickened cyst wall and a thickened vessel wall.
The cyst lining is composed of a single layer of eosinophilic cells with bland basally situated nuclei. Some cysts may be lined by squamous epithelium which may be keratinized. Columnar cells and cells with mucin have also been described.
Splenic cysts are either true cysts, which have an epithelial cell lining, or pseudocysts. The differential diagnosis of a cystic splenic mass is broad and includes a true cyst, posttraumatic pseudocyst, echinococcal cyst, hematoma, prior infarction, pyogenic abscess, and lymphangioma.
These cysts have also been reported to arise in accessory spleens.
These cysts are usually asymptomatic except in cases with a mass effect. They are usually fairly large (10 cm or greater) and unilocular. Thin fluid may be present in the lumen.
Complete excision.
There is the potential for hemorrhage or secondary bacterial infection.