
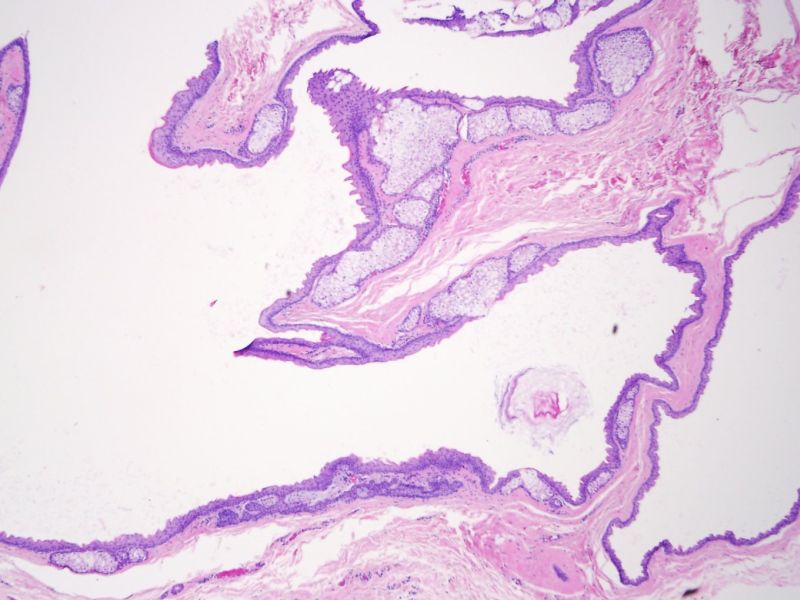
A steatocystoma is composed of ruggated squamous epithelium with a characteristic eosinophilic refractile cuticle of keratin in place of a granular layer. Sebaceous glands within the cyst wall open into the cyst. The cyst often appears empty because during processing of the tissue, the oily fluid dissolves (Rapini).
On higher power, one can see the characterisitic wrinkled refractile eosinophilic cuticle.
Steatocystomas occur as a solitary lesion ("steatocytoma simplex") or as part of an autosominal dominantly inherited, or sporadically ocurring condition, steatocytoma multiplex. In the latter, there is a mutation in the gene for keratin 17. Keratin 17 is expressed among various epithelial structures, including sebaceous glands. The mutation is identical that found in patients with pachyonychia congenita type 2, characterized by hypertrophic nail dystrophy, focal keratoderma, pilosebaceous cysts, and a variety of alterations associated with ectodermal dysplasia.
The lesions appear as numerous yellow or flesh colored dermal cysts, 3 mm to 3 cm which are often freely movable.
Rapini RP.Practical Dermatopathology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2005: 255-6.