
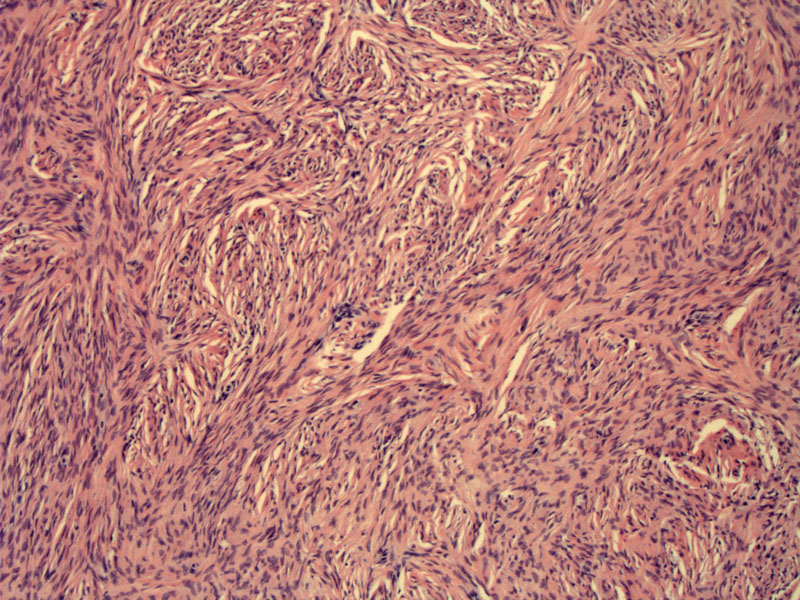
Fibromas are composed of fascicles of bland elongated spindle cells in a storiform or whorled pattern.
The cells are fusiform and elongated, embedded in a collagenous stroma. There is no cytologic atypia, and mitotic activity is rare.
A different case demonstrates prominent stromal calcifications. Calcifications can be found in fibromas, but they are more frequent in the setting of Gorlin syndrome.
Ovarian fibroma is the most common sex cord-stromal tumor, comprising approximately 70% of tumors in this category.1 They are tumors of middle-aged women and the vast majority are unilateral with the exception of fibromas in the setting of Gorlin syndrome. Gorlin syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder that manifests with nevoid basal cell carcinoma, skeletal abnormalities and bilateral ovarian fibromas.
Fibromas are composed of fascicles of elongated spindled cells set against moderately abundant collagenous stroma. In the cellular variant, there is increased cellularity with less intercellular stroma. This variant is often arranged in a herringbone or stitched pattern. If there is mitotic activity, the tumor may be termed "mitotically active cellular fibroma". Note that these tumors should only exhibit minimal cytologic atypia. In contrast, fibrosarcomas exhibit moderate to marked cytologic atypia and are generally mitotically active as well.
Most commonly seen in the 5th decade, however, they are seen earlier in women with Gorlin syndrome. The vast majority unilateral; bilateral tumors occur in 5-10% of cases. In Gorlin syndrome, the tumors tend to be bilateral and heavily calcified.
Fibromas are usually incidental findings, but patients may present with non-specific symptoms such as abdominal pain. Meigs syndrome (ascites and hydrothorax in the presence of an ovarian fibroma) can occur, especially if the tumor is greater than 10 cm.
Grossly, the tumor is well-circumscribed with a homogenous, firm white to yellow cut surface. Cellular variants tend to be more yellow. Cellular fibromas and fibrosarcomas also may contain focis of hemorrhage and necrosis.
Treatment is via surgical resection, typically with oophorectomy.
Benign. However, the cellular variant may be associated with recurrence and locally invasive growth. Fibrosarcoma has a very poor prognosis.
♣ Fibromas are tumors of middle-aged women and are usually unilateral.
♣ Histologically, they are composed of bundles of spindled cells with sparse mitotic activity and absent cytologic atypia.
♣ Fibromas with increased mitotic activity or cellularity are known variants, but the cytology remains benign. Only fibrosarcomas have moderate or marked cytologic atypia.
1 Fletcher CDM, ed. Diagnostic Histopathology of Tumors. 3rd Ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2007: 595.
2 Nucci MR, Oliva Esther. Gynecologic Pathology: Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier: 2009: 445-450.