
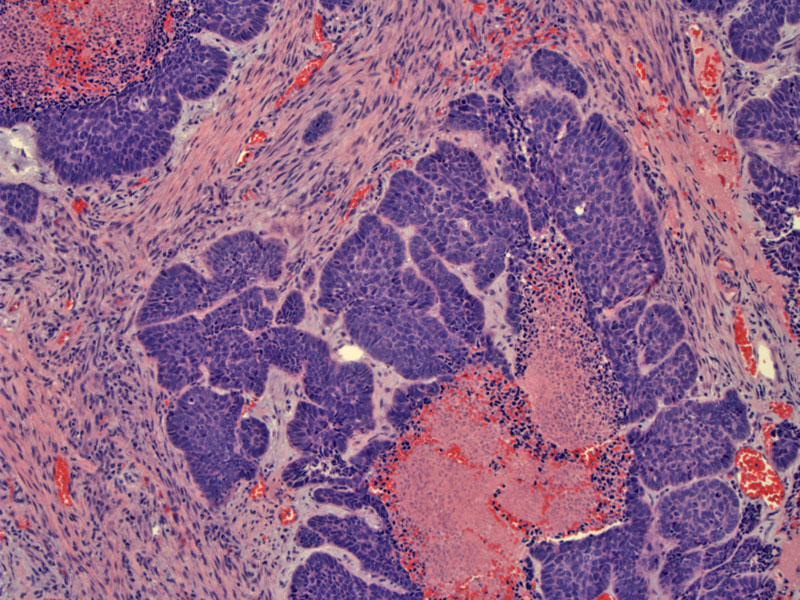
Nests of basaloid cells are set in a desmoplastic stroma with central comedo pattern necrosis.
Multiple lobules of basaloid cells emanate from the central necrosis. The cells have relatively scant cyoplasm and enlarged somewhat uniform malignant hyperchromatic nuclei.
The tumor shows peripheral, slightly elongated, palisaded cells surrounding each lobule and frequent mitoses.
Strong keratin 5/6 is seen in all basaloid squamous cell carcinomas (Serrano) as illustrated here. In contras,t only a minority of neuroendocrine carcinomas react for this marker, a feature which may be helpful in the differential diagnosis.
As seen in this image, basaloid squamous cell carcinomas consistently display diffuse p63 positivity, with staining of nearly 100% of tumor cells. In the event of potential confusion with adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC), you can examine the pattern of p63 reactivity, which in ACC shows a consistently compartmentalized pattern within tumor nests (Emanual). In solid nests of ACC, a distinct peripheral staining pattern is seen, while in cribriform areas, a combinations peripheral/internalization pattern is seen. Additionally, the p63-positive cells in ACC are predominantly smaller than the p63-negative cells, and appear to lack nucleoli http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15529180?itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum&ordinalpos=3
TTF-1 is negative (shown), as well as negative reactivity for chromogranin and synaptophysin. These features which may help distinguish this from small cell carcinoma in a small biopsy
Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma (BSCC) is regarded as a more aggressive variant of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) with a tendency to involve the tongue base, supraglottic larynx, the pyriform sinuses, esophagus, lungs, anal region, and uterine cervix. Areas of conventional SCC may be identified within the lesion.
Men are most often involved.
In the case of a resectable lesion with no evidence of metastasis, surgery should be the mainstay treatment as it offers a chance for cure. The basaloid component should not be considered a contraindication to surgery. In fact, one study found that the rates of loco-regional control are identical in both groups of patients (75% for the SCC and 74% for the less BSCC).Given the high rate of lymph node metastasis, neck dissection should be performed in all cases even in the absence of clinically or radiologically detectable lymph node enlargement1 .
The tumor typically has a oor prognosis, with rapid tumor growth and a low survival rate, independent of stage and other disease-related characteristics (Soriano). By comparison, those with usual SCC present a higher rate of loco-regional recurrence, while those with BSCC develop a higher rate of distant metastases1 .
• Oral Cavity : Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma (Tongue)
1 Soriano E, et al. Course and prognosis of basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a case-control study of 62 patients. Eur J Cancer. 2008 Jan;44(2):244-50. Epub 2007 Dec 21.
2 Thariat J, Ahamad A, El-Naggar AK, Williams MD, Holsinger FC, Glisson BS, Allen PK, Morrison WH, Weber RS, Ang KK, Garden AS. Outcomes after radiotherapy for basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a case-control study. Cancer. 2008 Jun 15;112(12):2698-709.
3 Serrano MF, El-Mofty SK, Gnepp DR, Lewis JS Jr. Utility of high molecular weight cytokeratins, but not p63, in the differential diagnosis of neuroendocrine and basaloid carcinomas of the head and neck. Hum Pathol. 2008 Apr;39(4):591-8. Epub 2008 Mar 4.
4 Emanuel P, Wang B, Wu M, Burstein DE. p63 Immunohistochemistry in the distinction of adenoid cystic carcinoma from basaloid squamous cell carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2005 May;18(5):645-50.